TSOC-MSGL
 Disturbance event
Disturbance eventSummary
The Cyprus grid’s rising inverter-based renewable penetration reduces synchronous inertia and fault current, tightening frequency margins and stressing protection and stability, especially after large contingencies. This work proposes a rigorous, multi-stage methodology to resize and coordinate inertia, FFR, FCR, FRR, and RR so frequency nadir, RoCoF, and recovery remain within secure limits while meeting N-1, system strength, and LVRT criteria. The outcome is a transparent, reproducible framework that identifies acceptable unit-commitment scenarios and operating margins that balance RES integration with security needs.
Project Objectives
- Operating Margin Assessment: Structured review of inertia adequacy, fault-level sufficiency, and N-1 security to update TSOC’s operating margin policy under high-RES conditions.
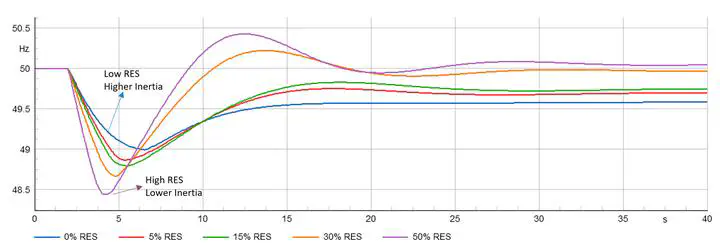
- Frequency Security Enhancement: Enforce RoCoF, nadir, and quasi-steady-state frequency limits by combining physical and virtual inertia with rapid services like FFR.
- Reserve Sizing Optimization: Dimension FFR, FCR, FRR, and RR alongside inertia so nadir and steady-state limits are satisfied under credible loss events and diverse operating points.
- Policy Recommendations: Provide minimum synchronous generator requirements and coordination rules with emerging products (e.g., grid-forming, FFR) to sustain security with more RES.
Methodology
Theoretical Analysis
- System Limits Calculation: Derive minimum kinetic energy for a given RoCoF limit and credible loss, compute nadir and quasi-steady-state deviations, and include virtual inertia from grid-forming units.
- Reserve Requirements Assessment: Link FFR/FCR contributions with inertia to keep nadir above UFLS thresholds and steady-state deviation within permissible bounds.
Dynamic Simulations
- Time-Domain Analysis: RMS simulations of three-phase faults with 150 ms clearing at critical 132 kV buses to verify transient stability, synchronism, and recovery.
- Scenario Analysis: Evaluate clustered representative operating points and feasible unit-commitment sets against N-1 and dynamic constraints.
- Performance Metrics: Check RoCoF ≤ 1 Hz/s, nadir within limits, CCT margin, damping/recovery, and LVRT compliance per grid code curves.
Probabilistic Techniques
- Risk Assessment: Use worst-case non-inertial loss (e.g., 120 MW) and largest committed SG loss to screen combinations against RoCoF and nadir risks.
- Monte Carlo Simulations: Apply operating-point clustering and multi-scenario checks to capture variability in demand/RES dispatch and contingencies.
- Reliability Indices: Track pass/fail across filters (RoCoF, MSGL, fault-level/SCR, N-1, LVRT/TSM) as security indicators for policy formulation.
Machine Learning Approaches
- Data-Driven Optimization: Reduce search space via generator clustering tolerances and operate-point clustering to enable tractable screening and sizing.
- Dynamic Security Assessment: Automate DIgSILENT-driven N-1 and RMS workflows with binary filters for acceptable scenarios across centroids.
- Pattern Recognition: Identify recurring weak-grid locations (low SCR, voltage stiffness) and operating patterns that require higher inertia/FFR.
Key Findings
- Fast Frequency Response (FFR) Optimization: Explicitly links FFR and inertia to nadir control under worst-case losses; 0.8 s response requirement supports nadir without overcommitting SGs.
- Operating Margin Redefinition: Fixed must-run rules can be replaced by an evidence-based set of acceptable UC scenarios satisfying RoCoF, MSGL, SCR, N-1, and LVRT constraints.
- Reserve Coordination: Coordinated inertia, FFR, and FCR ensure nadir and steady-state targets simultaneously, with dynamic checks validating viability under severe faults.
- System Resilience: Enforcing fault-level and SCR thresholds at HV buses/substations prevents protection misoperations and IBR control instabilities in weak-grid pockets.
Impact and Outcomes
- Policy Development: Provides a monthly planning workflow to choose secure UC scenarios, informing TSOC operating margins and minimum synchronous generator levels.
- Operational Guidelines: Codifies sequential filters (RoCoF → MSGL → fault-level/SCR → N-1 → transient/LVRT) and simulation settings for DIgSILENT-based assessment.
- Research Advancement: Documents analytical formulas, clustering thresholds, and LVRT assessment logic to support method generalization and publication.
- Industry Collaboration: Aligns grid-code constraints (e.g., RoCoF, LVRT, CCT) and operational practices with TSOC needs under accelerating RES integration.
Related Publications
The methodology underpins work on optimal FFR and inertia co-sizing for nadir security in low-inertia grids, connecting analytical limits with DSA-backed validation at realistic operating points.
Industrial contacts
- Vrahimis Koutsoloukas (TSOC)
- Christos Frangkeskou (TSOC)